Digital healthcare and the challenges to construction cost management
The cost of delivering high-quality healthcare continues to increase every year, and as a result, the pressure to deliver high-quality and affordable hospital facilities has never been greater.
The construction budgeting and Cost Management of acute healthcare facilities has always presented those in charge of their delivery with significant challenges.
This is as a result of a number of factors:
- Length of time from project inception to handover
- Level of complex building services systems required
- Changing standards
- Changes in project brief requirements
- Impact of construction/tender inflation.
However, while developments in technology, both in general and within the Healthcare sector specifically, are adding additional challenges and levels of complexity, they are also offering distinct benefits. Some examples of technology application in a healthcare environment include:
Hybrid theatres
The hybrid operating theatre combines a conventional operating theatre with imaging systems such as MRI, CT or angiography.
Intraoperative magnetic resonance imaging refers to an operating room configuration that enables surgeons to image the patient via an MRI scanner while the patient is undergoing surgery. It is used in cases of brain surgery in particular.
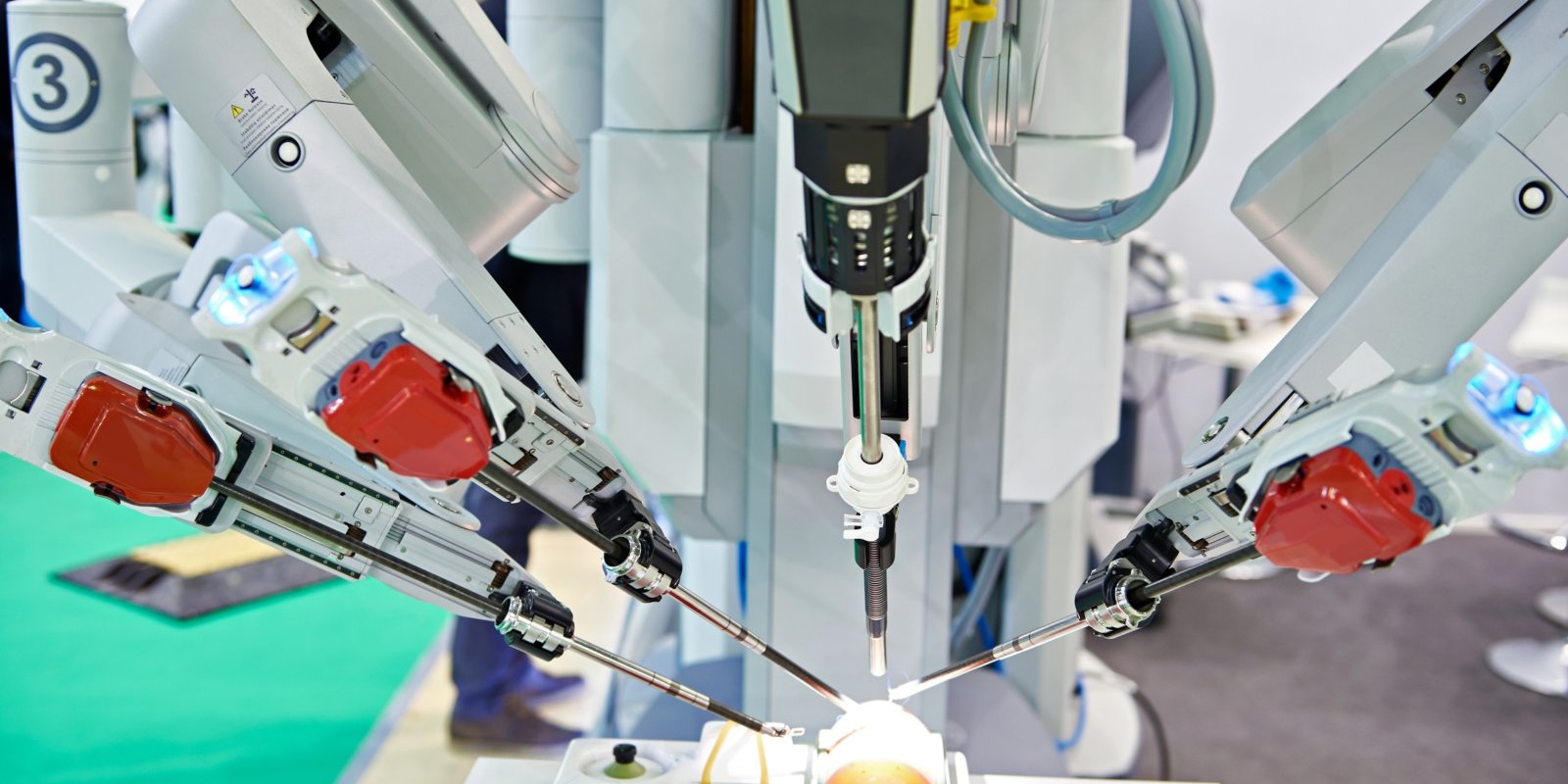
Surgical robotics
Surgical robots have moved out of sci-fi movies and the distant future, and have arrived in the modern operating theatre. Robotic-assisted surgery involves a skilled surgeon working with advanced technology.
These surgical robots are changing the face of healthcare delivery by allowing surgical operations to be carried out with greater precision, and allowing remote surgery where the physician is not present physically with the patient.
UV disinfection robots
With ultraviolet light technology, these robots disinfect a specific area within minutes and make it free of viruses, bacteria etc. These robots move anywhere inside the room and target a predefined area.
Automated guided vehicles (AGV)
AGVs are recognized as having the potential to play a vital part in delivering efficiencies and savings to hospitals, in terms of operational procedures.
There are a number of design considerations to be considered:
- Space planning and the additional area requirements
- Interface with other systems such as doors, lift access control systems, fire alarm systems etc.
- Impact on hospital operational policies
Pharmacy robotic systems
A pharmacy robotic system is an automated distribution system that provides computer controlled storage, dispensing and tracing of medication.
The ‘digital’ or ‘smart’ hospital
A ’digital’ or ‘smart’ hospital relies on optimized and automated processes, and is built upon an ICT environment of interconnected assets targeted at improving patient care procedures. The ’digital hospital’ concept is developing, and is introducing new operational policies and methods of service delivery, which are being reflected in the hospital designs.
The ’digital hospital’ includes the following:
- Paperlite facility - Buildings that utilize technology systems to streamline and automate processes, and reduce reliance on paper-based systems.
- Self-service kiosks - Providing quick and easy check-in for patients.
- Patient edu-tainment systems - Providing patient healthcare information, entertainment, food ordering and school education.
- Wireless technology - Supporting the digital and wireless strategies of the hospital.
- Electronic healthcare records - Allowing patient medical information to be captured once, and to then be available to the patient and clinical staff.
Procurement
An outcome of these technological developments is that the procurement options for healthcare equipment are being reviewed. One of the options for medical equipment procurement which is becoming more common is a Managed Equipment Service (MES). The service typically covers a period of 10-25 years, depending on the particular equipment, and covers installation, commissioning, user training, asset management and ongoing replacement.
Soft landings
As buildings become more complex, the handover between construction and operation is changing.
‘Soft landings’ is a process utilized throughout the project design and construction, to improve operational readiness and performance in use. During the construction process, the contractor, in conjunction with the client and design team, will prepare for a seamless transition of the employer into the occupancy and operation of the building. The process will facilitate the involvement of key client personnel in the graduated sign-off of building areas over the entire commissioning period through to substantial completion and initial occupancy of the hospital, and is designed to assist the clinicians and building users in getting the best out of their new building.
Building Information Modelling
While technology and digital developments have presented challenges, as noted earlier, they are also providing solutions to the design team, and in particular the Quantity Surveyor. Through BIM, we are now see the emergence of the 5D Quantity Surveyor, where the focus is moving to the collection and analysis of high-quality data, in order to provide more accurate and up-to-date information to clients and other design team members.
One of the most significant benefits we have seen to date is the project and data analysis, which we can now carry out and apply to areas such as model development tracking, clash analysis, and area analysis. In addition, the use of 3D information allows us to collect data, and to advise and assist clients with future project development planning.
Future proofing
One of the key challenges in the delivery of a digital hospital is how you design a technology-enabled facility that can maintain its currency, not only from hospital design to deployment, but also over the 20 to 50 years of its total lifespan. However, the question remains as to how design can be sufficiently flexible, to facilitate evolving technology?
In summary, while digitalization can pose additional challenges and complexity, there is little doubt that technological developments are offering distinct benefits for healthcare facilities. As the ‘digital hospital’ continues to evolve in line with technology, we expect to see continuing improvements in patient care procedures and operational policies.






